Stepper Motor:
1.Permanent magnet (PM) stepper motor:
2.Variable reluctance (VR) stepper motor:
3.Hybrid Synchronous stepper motor:
1.Unipolar stepper motor:
2.Bipolar stepper motor:
Raspberry Pi:
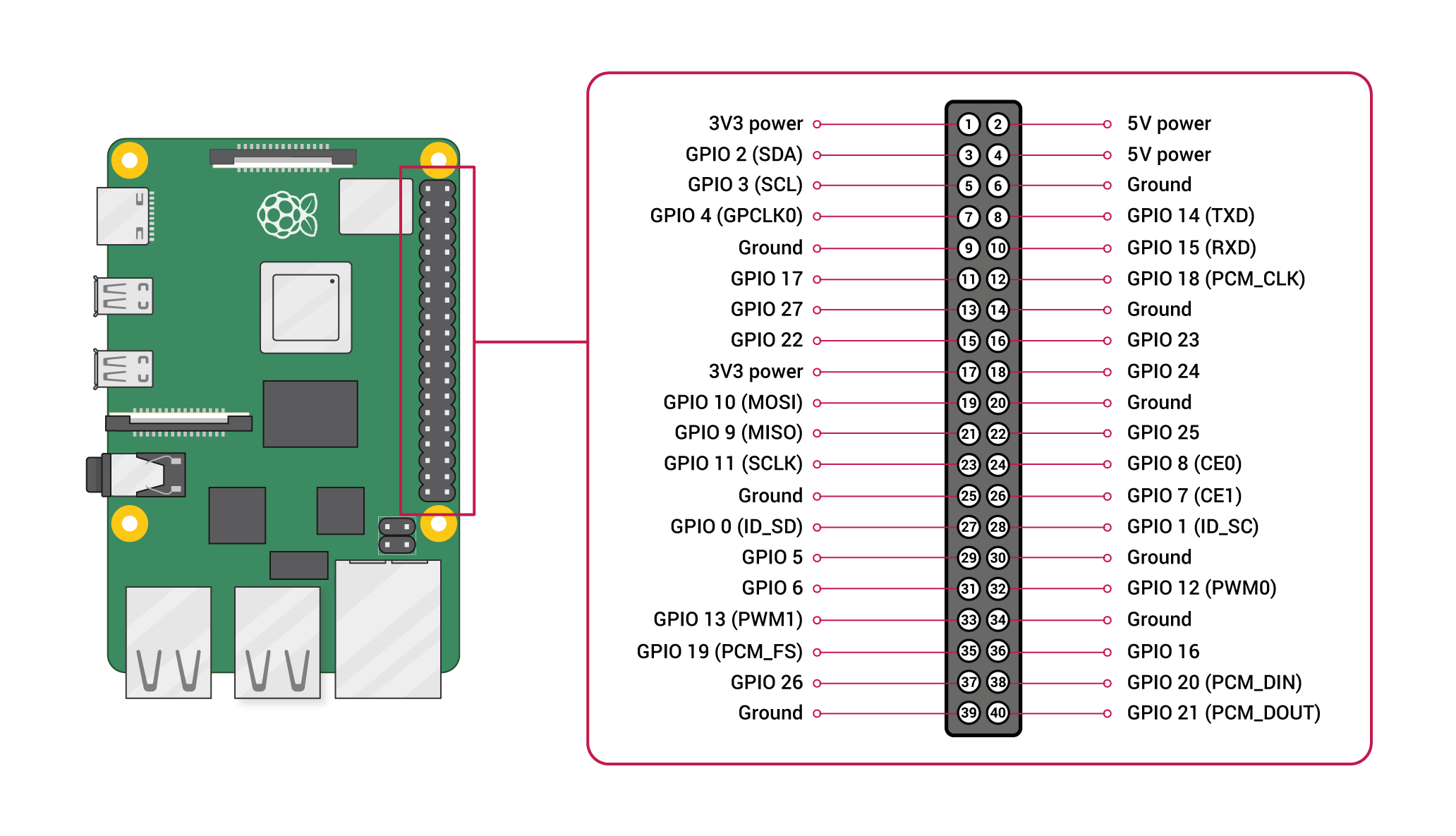
Pin configuration:
1. Vin: Two 5v pins and two 3v3 pins used for providing power supply, where processor works on 3.3v.
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO import time GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) GPIO.setup(16, GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(18, GPIO.OUT) While 1: x = 1 GPIO.OUTPUT(16, 1) # SETS THE MOTOR CLOCK-WISE DIRECTION for x in range(200): GPIO.OUTPUT(18, 1) time.sleep(0.5) GPIO.OUTPUT(18, 0) time.sleep(0.5) time.sleep(1) GPIO.OUTPUT(16, 0) # SETS THE MOTOR ANTI-CLOCK-WISE DIRECTION for x in range(400): GPIO.OUTPUT(18, 1) time.sleep(0.5) GPIO.OUTPUT(18, 0) time.sleep(0.5) time.sleep(1)
